|
GEOCHEMICAL FEATURES, SOURCES OF SUBSTANCE AND AGE TO BITU-DZHIDA MULTIPHASE INTRUSION OF Li-F GRANITES (KHAMAR-DABAN) Perepelov A.B., Tatarnikov S.A., Dril S.I., Antipin V.S., Vladimirova T.A., Sandimirova G.P. Institute of Geochemistry SB RAS, Irkutsk, Russia, region@igc.irk.ru The purpose of the given work is to show results of the newest geological and isotope-geochemical studies of the Bitu-Dzhida multiphase intrusion of Li-F granites, located in southern spurs of Khamar-Daban Ridge (51003′20″N, 102011′20″E). The Bitu-Dzhida intrusion is found in the Upper Proterozoic metamorphic sequence (crystalline schist of the Bitu-Dzhida suite). The massif was discovered in 1933 (Naletov, 1941) and later studied via geologic survey and prospecting for Li, Rb, Ta, Nb (1954-1960) as well as via systematic scientific researches (Koval, 1975; Kosals, 1976). Using K-Ar of dating the age of the massif was determined as the Permian-Triassic - 262-218 Ma (Kosals, 1976). By the results of recent investigations (Perepelov et al, 2007) we can distinguish three main phases of intruding granite magma. The 1st phase includes small outcrops of Pl-Kfs-Qtz-Bt middle-grained and porphyry-like granites; 2nd phase comprises Qtz-Kfs-Pl-Bt leucocratic granites. And the predominant are amazonite-albite-zinnwaldite (Amz-Ab) rare-metal granites of the final 3rd phase. Pegmatite-formation and greisening took place at the terminating stage of the intrusive massif formation. Exocontact zones show cataclasm, crushing and recrystallization of crystalline schist.
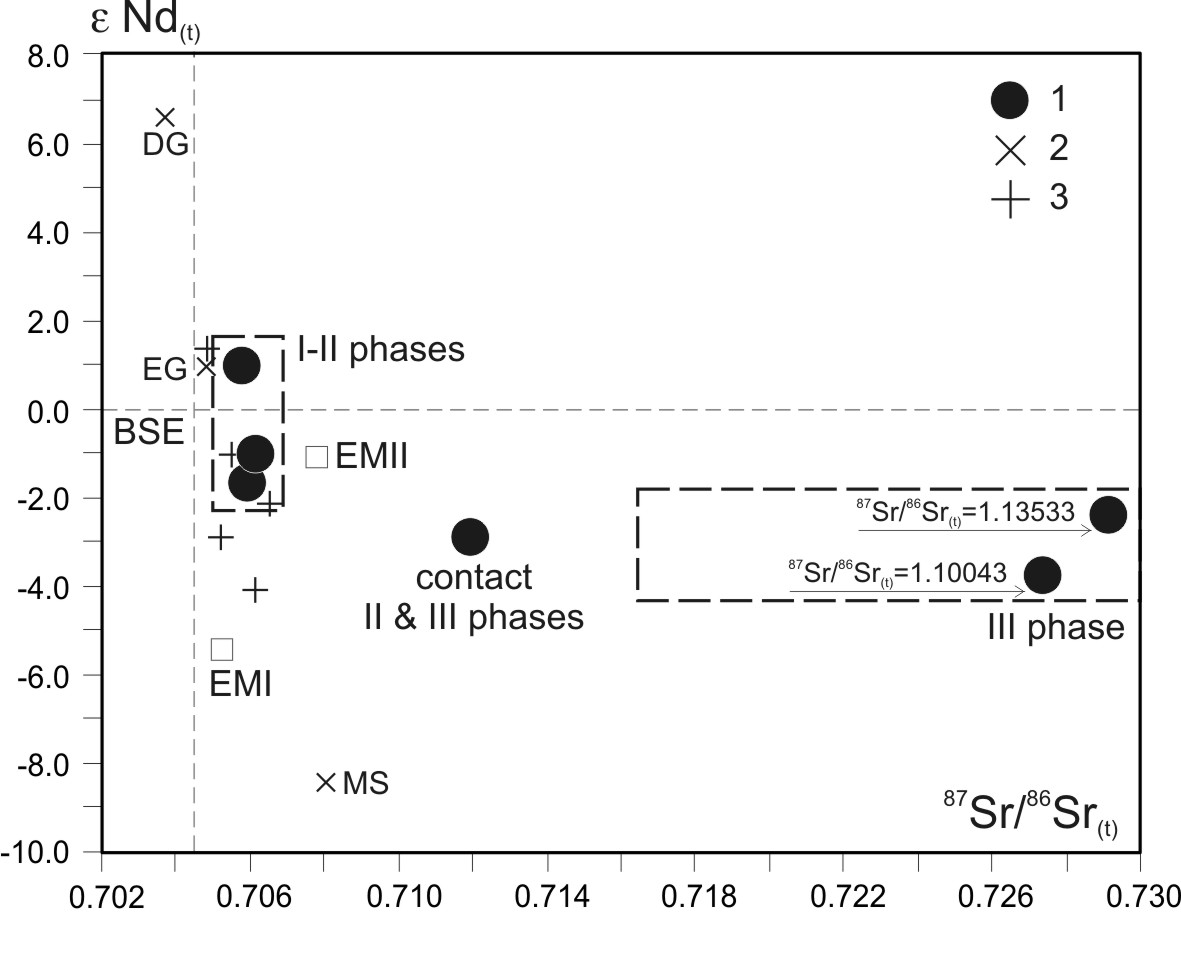
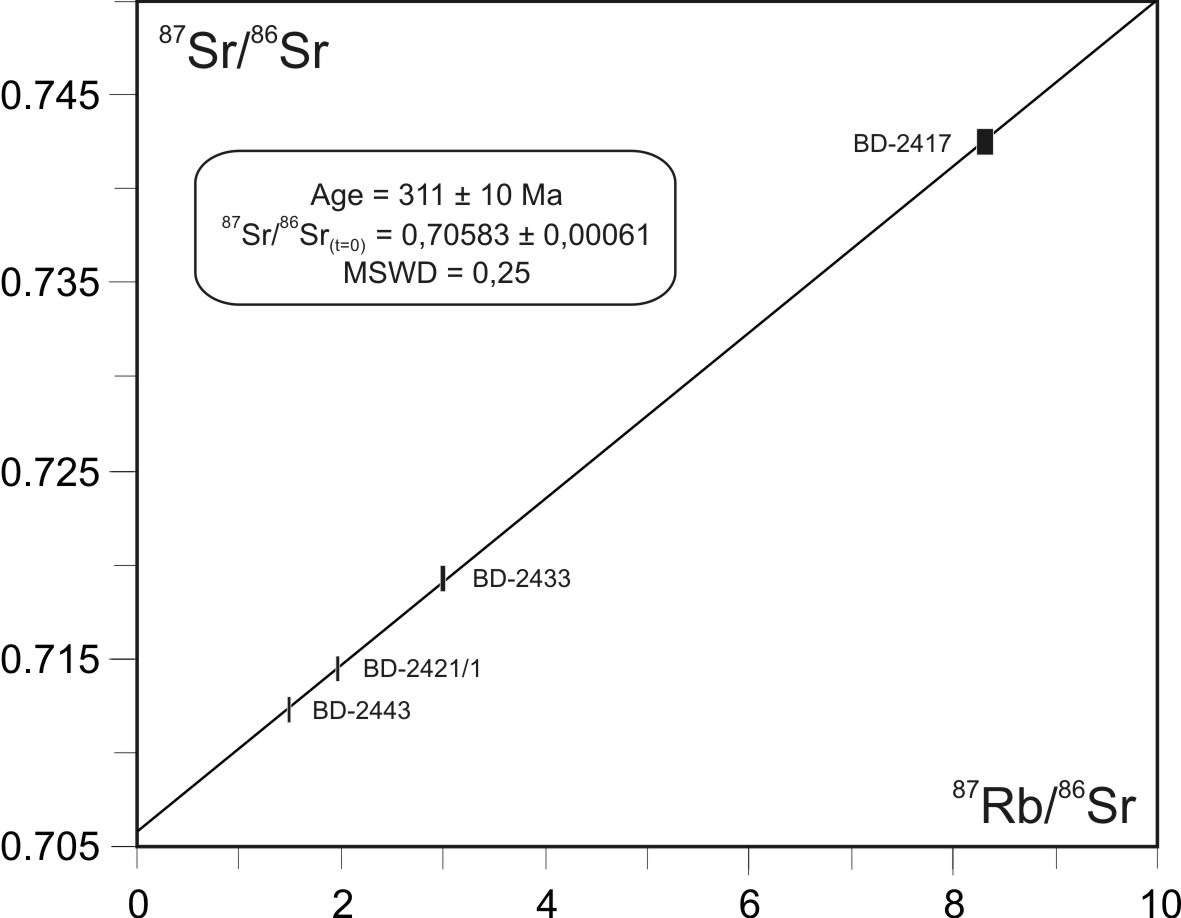
Rocks of all three intrusive phases of the massif belong to group of plumasite granites of Li-F geochemical type. Concentration of rare elements, namely Li, F, Sn, Ga, Rb, Nb, Ta, Pb, Th and U increase in rocks successive to intrusive phases. Compositions of rocks of the early phase differ from granites of the 2nd and 3rd phases in lower silica content and the lowest total alkalinity. Granites of the 1st phase have the most differentiated REE distribution spectra (LaN/YbN 10.6-16.3 ) while the rocks of the 2nd intrusive phase show decrease in REE fractionation (LaN/YbN 3.6-6.6) resulting from an essential enrichment by heavy elements of the spectrum and possess more considerable deficiency EuN (Eu* 0.18-0.29 as compared to 0.49-0.65 for rocks of the 1st phase). Amz-Ab leucogranites of the final 3rd phase are characterized by a sharp LREE depletion (La/Yb <1) and a deep Eu-minimum (Eu*0.05). Distribution pattern of rare elements including REE, correspond to models of crystallization differentiation of initial magma when granites of the 2nd intrusive phase generated. The model of forming Amz-Ab rare-metal granites of the 3rd phase is associated with fluid-magmatic liquation processes. According to new data, the time of intruding the 1st initial phase of granitoids of the Bitu-Dzhida intrusion is regarded as the Late Carbonaceous (С2) that is 311 ± 10 Ma (Fig. 1). These data allow considering the studied intrusive complex as belonging to the age group of the Urugudeev (321 ± 5 Ma) and Kharagul (318 ± 3 Ma) massifs of Li-F granites of Khamar-Daban ridge (Kostitsyn, 2002).
The obtained isotope characteristics for granitoids of the
1 Studies were supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, grants №№ 08-05-90201-Мong_а, 08-05-00403_а.
References Barry T.L., Saunders A.D., Kempton P.D., Windley B.F., Pringle M.S., Dorjnamjaa D., Saandar S. Petrogenesis of Cenozoic Basalts from Mongolia: Evidence for the Role of Asthenospheric versus Metasomatized Lithospheric Mantle Sources. J. Petrology. 2003. V. 44. № 1. P.55-91. Dobosi G., Kempton P.D., Downes H., Embey-Isztin A., Thirlwall M., Greenwood P. Lower crustal granulite xenoliths from the Pannonian Basin, Hungary. Part 2: Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf and O isotope evidence for formation of continental lower crust by tectonic emplacement of oceanic crust. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2003. V. 144. P.671–683. Hart S.R., Hauri E.H., Oschmann L.A., Whitehead J.A. Mantle plumes and entrainment: isotopic evidence. Science. 1992. V. 256. P.517-520. Kovalenko V.I., Kostitsyn Yu. A., Yarmolyuk V.V., Budnikov S.V., Kovach V.P., Kotov A.B., Salnikova E.B., Antipin V.S. Magma Sources and the Isotopic (Sr and Nd) Evolution of Li-F Rare-Metal Granites. Petrology. 1999 V. 7. № 4. P.383-409. Koval P.V. Petrology and geochemistry of albitized granites Novosibirsk: Nauka. 1975. 258p. Kosals Ya. A. Geochemistry of amazonite granites. Proceedings of the Institute of geology and geophysics, SB USSR Academy of Sciences. Issue 219. Novosibirsk: Nauka. 1976. 190p. Kostitsyn Yu. A. Origin of rare-metal granites: isotope-geochemical approach. PhD Thesis. Moscow: ONTI GEOKHI, Russian Academy of Sciences. 2002. 43p. Naletov P.I., Shalaev K.A., Deulya T.T. Geology of Dzhida ore area. Proceedings of VSGU. Issue. 27. Irkutsk. 1941. 282p. Perepelov A.B., Tatarnikov S.A., Antipin V. S, Dril S.I. Bitu-Dzhida massif(Southern Pribaikalye): geochemical evolution and ore potential of multiphase intrusion of granitoids of Li-F type. Problems of geochemistry of endogenous processes and environment. Proceedings of the All-Russia Scientific conference. V. 2. Irkutsk. P.181-185.
|